- Startseite
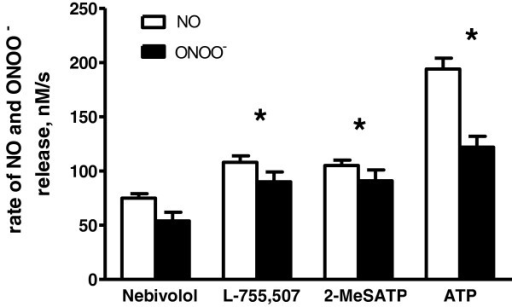
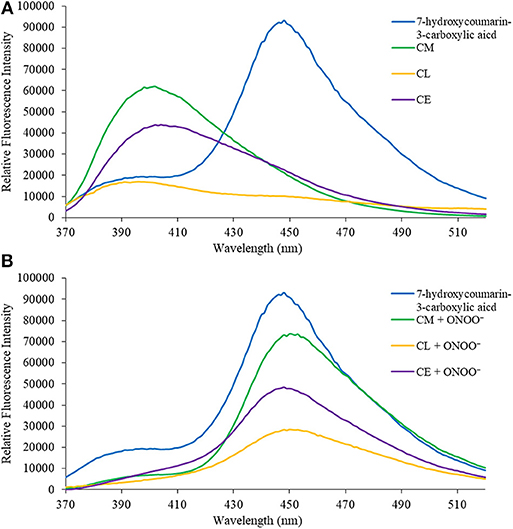
- onoo 2
- The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling
5 (768) · € 36.00 · Auf Lager
Protease-activated receptors (PARs) and the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. In this review, we focus on the regulatory mechanism of ectodomain shedding by ADAM10/17 metalloprotease via GPCR signaling. PAR2 and NK1R induce membrane blebbing, resulting in phosphatidylserine externalization in the cellular membrane, which is required for ADAM10/17 metalloprotease activation.

Roles of NS1 Protein in Flavivirus Pathogenesis

A model for ectodomain shedding and secretion of DPF. DPF is
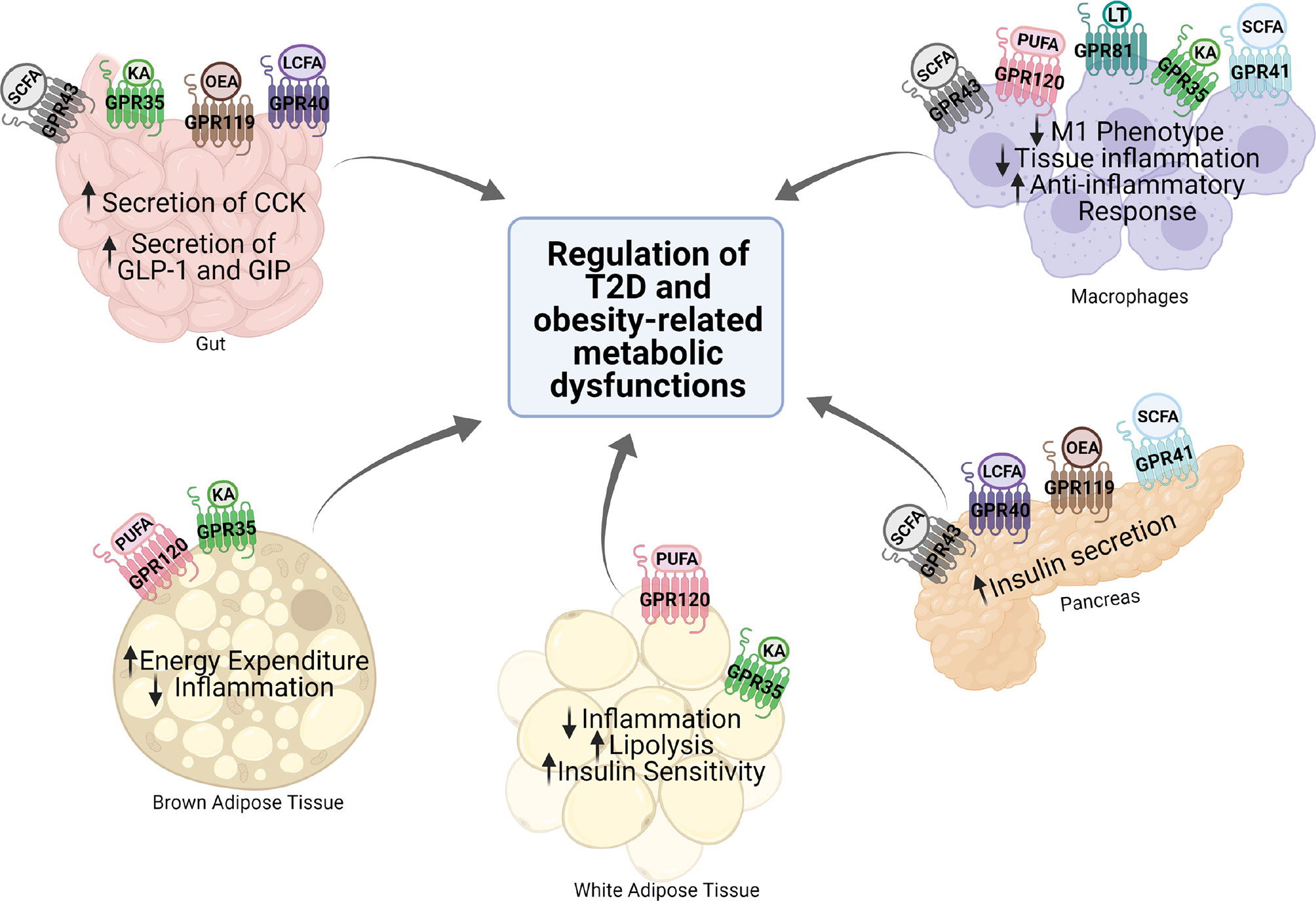
Frontiers Metabolic Functions of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and β-Arrestin-Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity

Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology

Ontogeny, Anatomy, Metabolism and Physiology of the Thyroid - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Intercellular signaling by ectodomain shedding at the synapse: Trends in Neurosciences

Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology

Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology

TRIM28/TIF1β and Fli-1 negatively regulate peroxynitrite generation via DUOX2 to decrease the shedding of membrane-bound fractalkine in human macrophages after exposure to substance P - ScienceDirect

Analysis of CERK1 ectodomain shedding and the role of XLG2 in cerk1-4 cell death execution