- Startseite
- onoo 2
- Antioxidant Mechanisms in Myocardial Ischemia: Narrative Review, Multidisciplinary Cardiovascular Annals
Antioxidant Mechanisms in Myocardial Ischemia: Narrative Review, Multidisciplinary Cardiovascular Annals
4.7 (590) · € 26.99 · Auf Lager
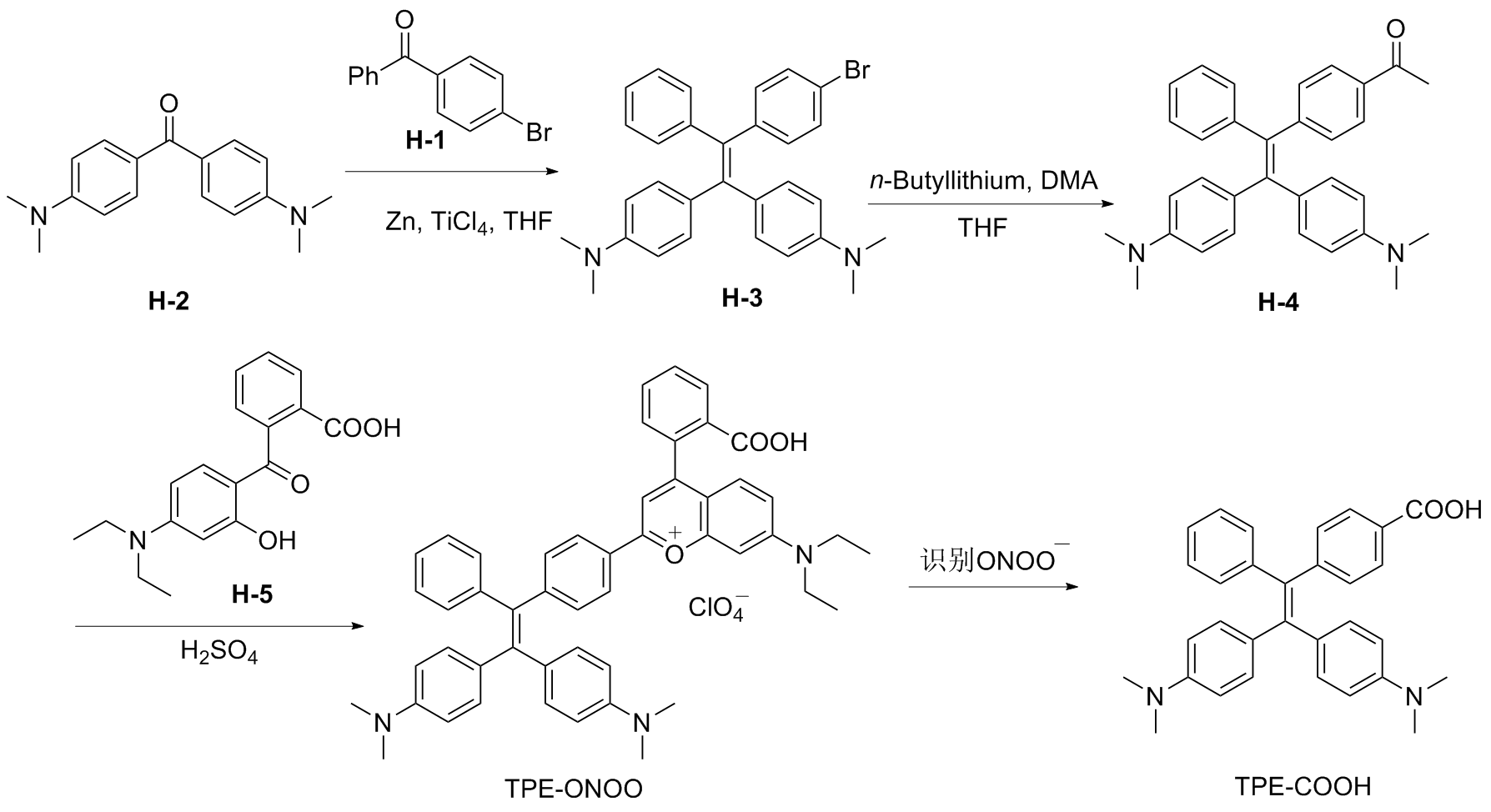
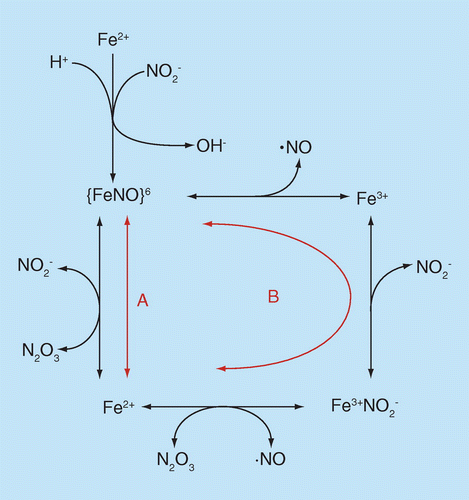
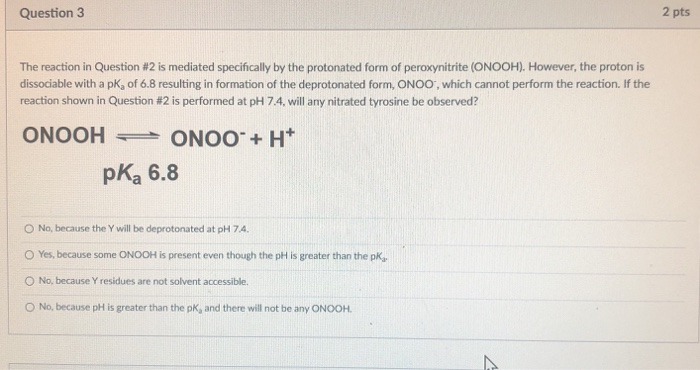
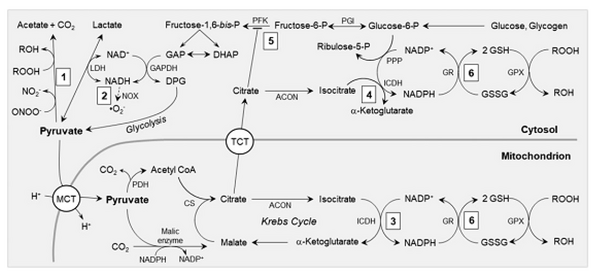
Ischemia is a common condition in the population and has become one of the leading causes of mortality in recent years. It occurs due to a shortage of oxygen in the cell caused by inadequate blood flow, leading to the formation of free radicals. These free radicals can bind to the phospholipids in the cell membrane, resulting in proxy radicals and lipid hydroperoxidation. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a cytotoxic byproduct of lipid peroxidation that causes cell damage and necrosis by rupturing the cell membrane. Subsequently, mitochondrial dysfunction related to fatty acid oxidation can develop, further exacerbating the damage caused by ischemia. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in mitochondria have been shown to elevate oxidative phosphorylation disorder and disrupt the functioning of complexes I and IV. These enzyme activities can be restored to normal levels by activating antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) and catalase, thereby strengthening the antioxidant defense system. Various antioxidants have been found to have protective effects. In this review, we compare the antioxidant effects of various plants and tannins that have been studied up to this point on myocardial ischemia. We also explain some of the cellular and molecular pathways that have been investigated to protect the myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury.

Prevalence and Impact of Myocardial Injury in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Infection
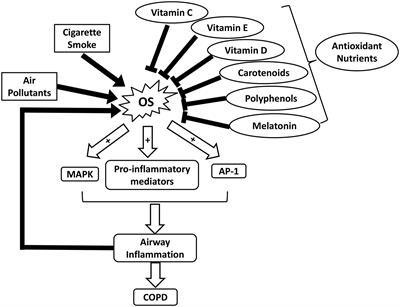
Frontiers Role of ROS and Nutritional Antioxidants in Human Diseases

Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
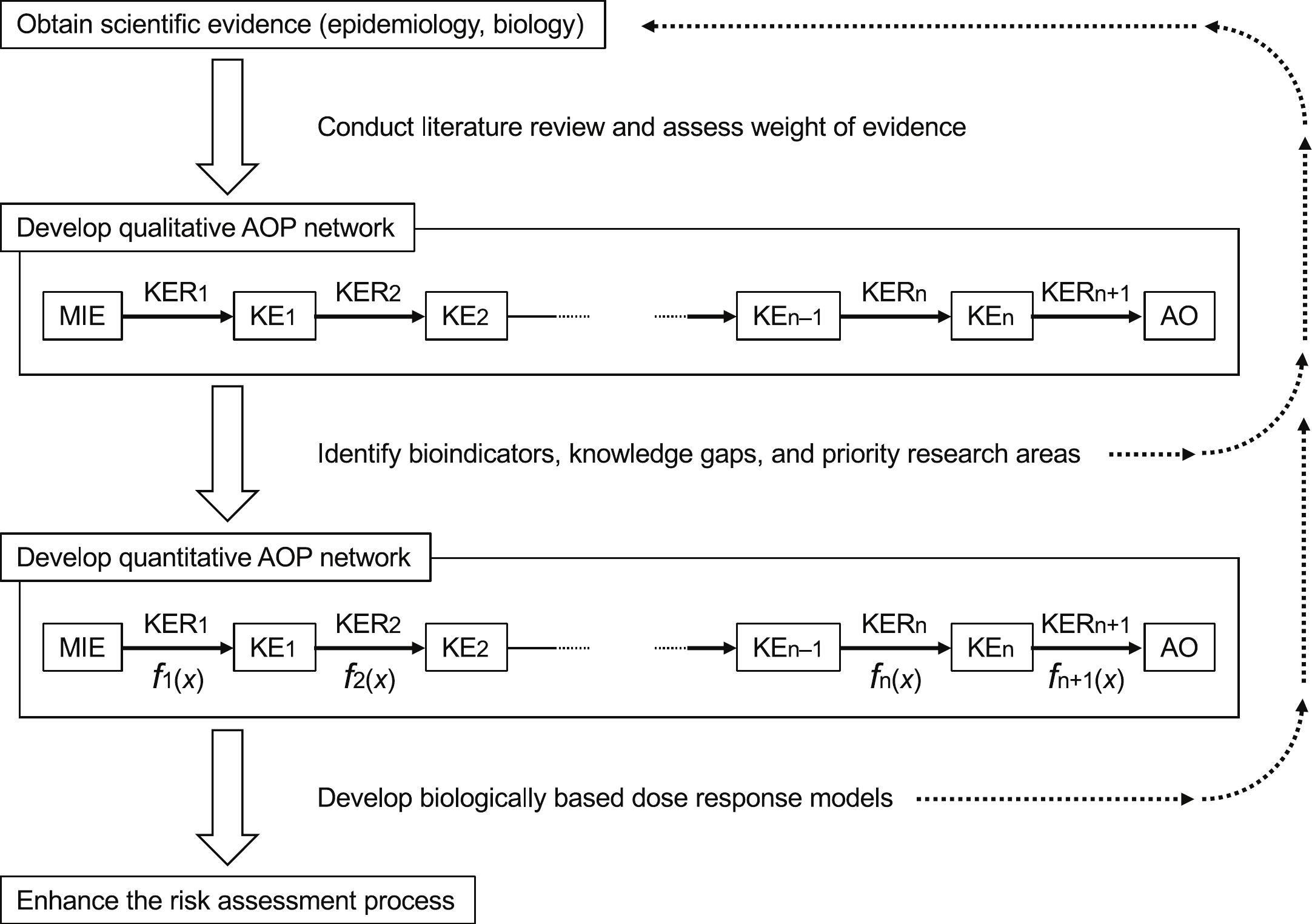
Noncancer Effects of Ionizing Radiation Exposure on the Eye, the Circulatory System and beyond: Developments made since the 2011 ICRP Statement on Tissue Reactions

Sleep Apnea: Types, Mechanisms, and Clinical Cardiovascular Consequences
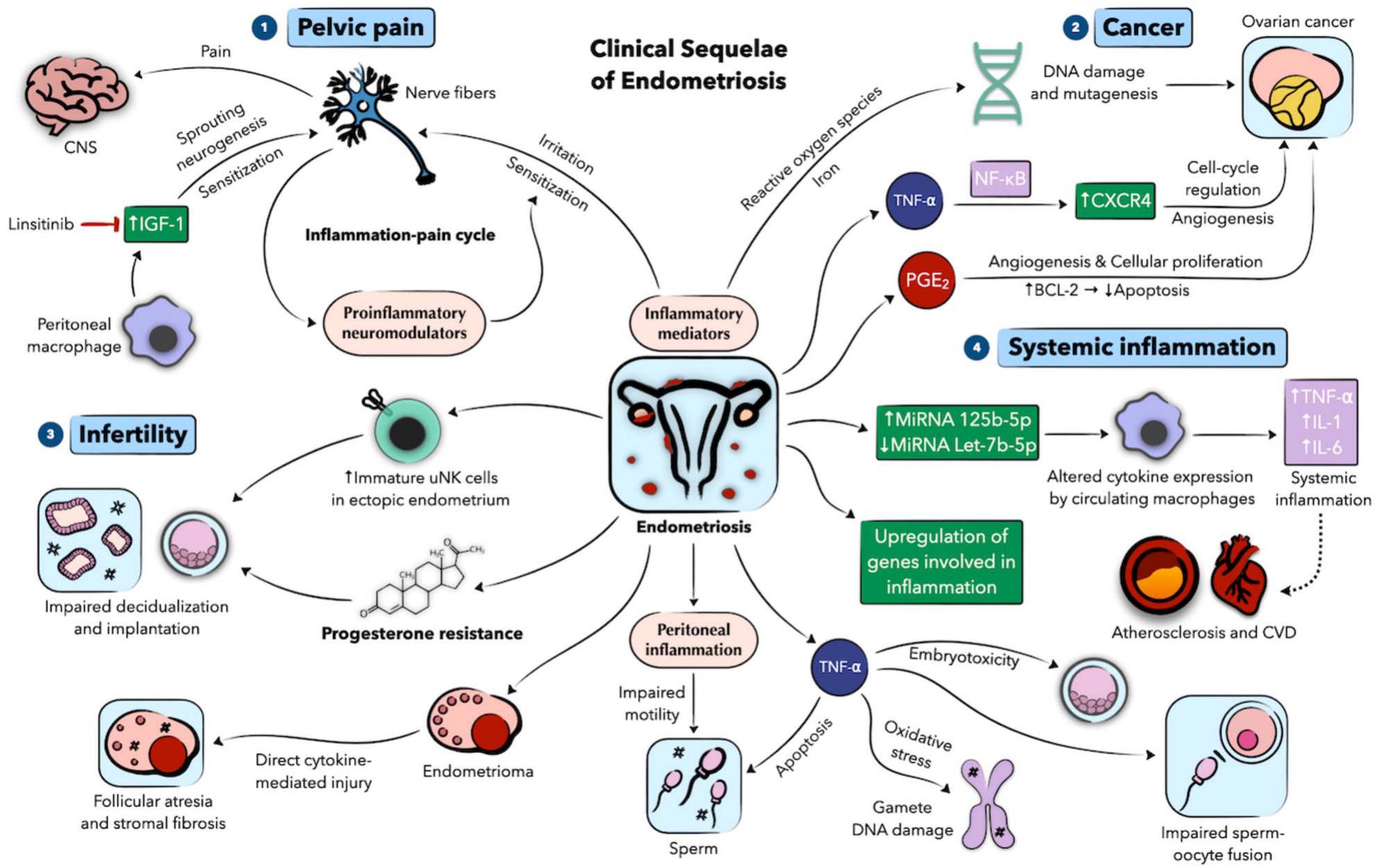
Role of inflammation in benign gynecologic disorders: from pathogenesis to novel therapies†
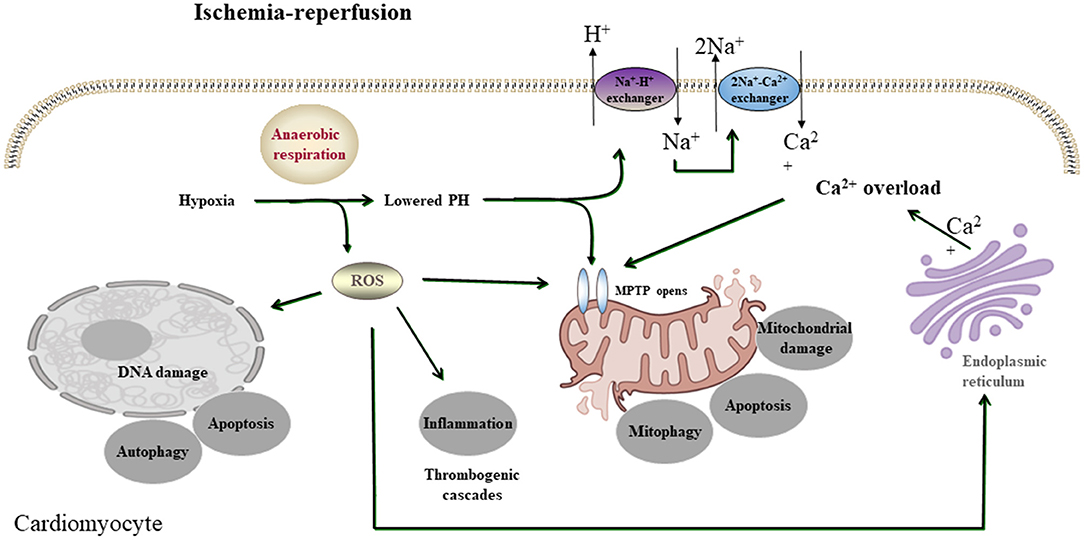
Frontiers Promising Therapeutic Candidate for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: What Are the Possible Mechanisms and Roles of Phytochemicals?
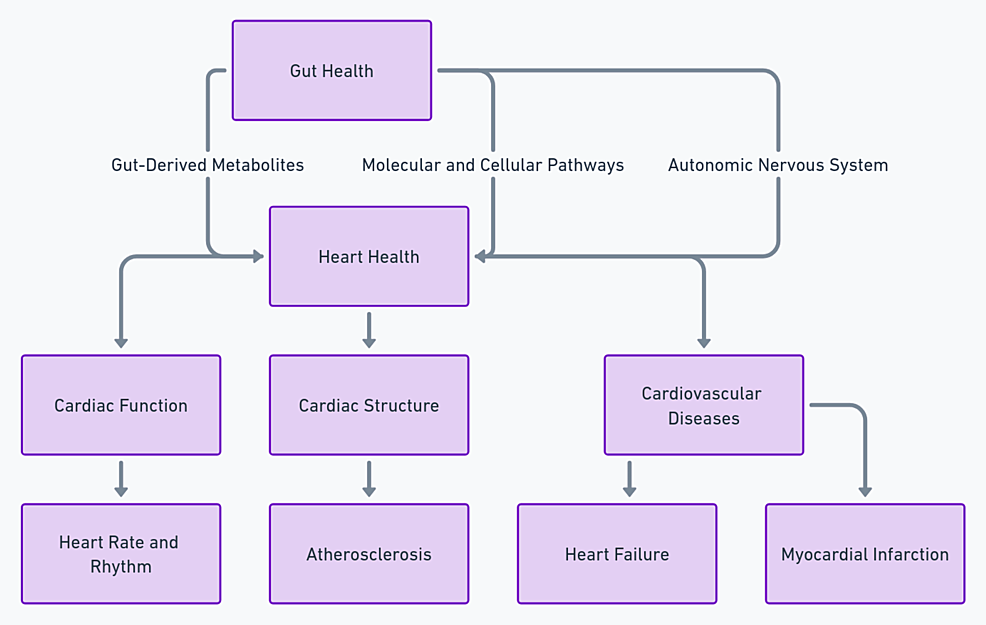
Cureus, Unlocking the Gut-Cardiac Axis: A Paradigm Shift in Cardiovascular Health

Nanozyme‐Enabled Treatment of Cardio‐ and Cerebrovascular Diseases - Zhang - 2023 - Small - Wiley Online Library

Target Fishing Reveals a Novel Mechanism of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives Targeting Rpn6, a Subunit of 26S Proteasome

Full article: Antioxidants in the prevention of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Cardioprotective mechanism of medicinal plants/herbal products on
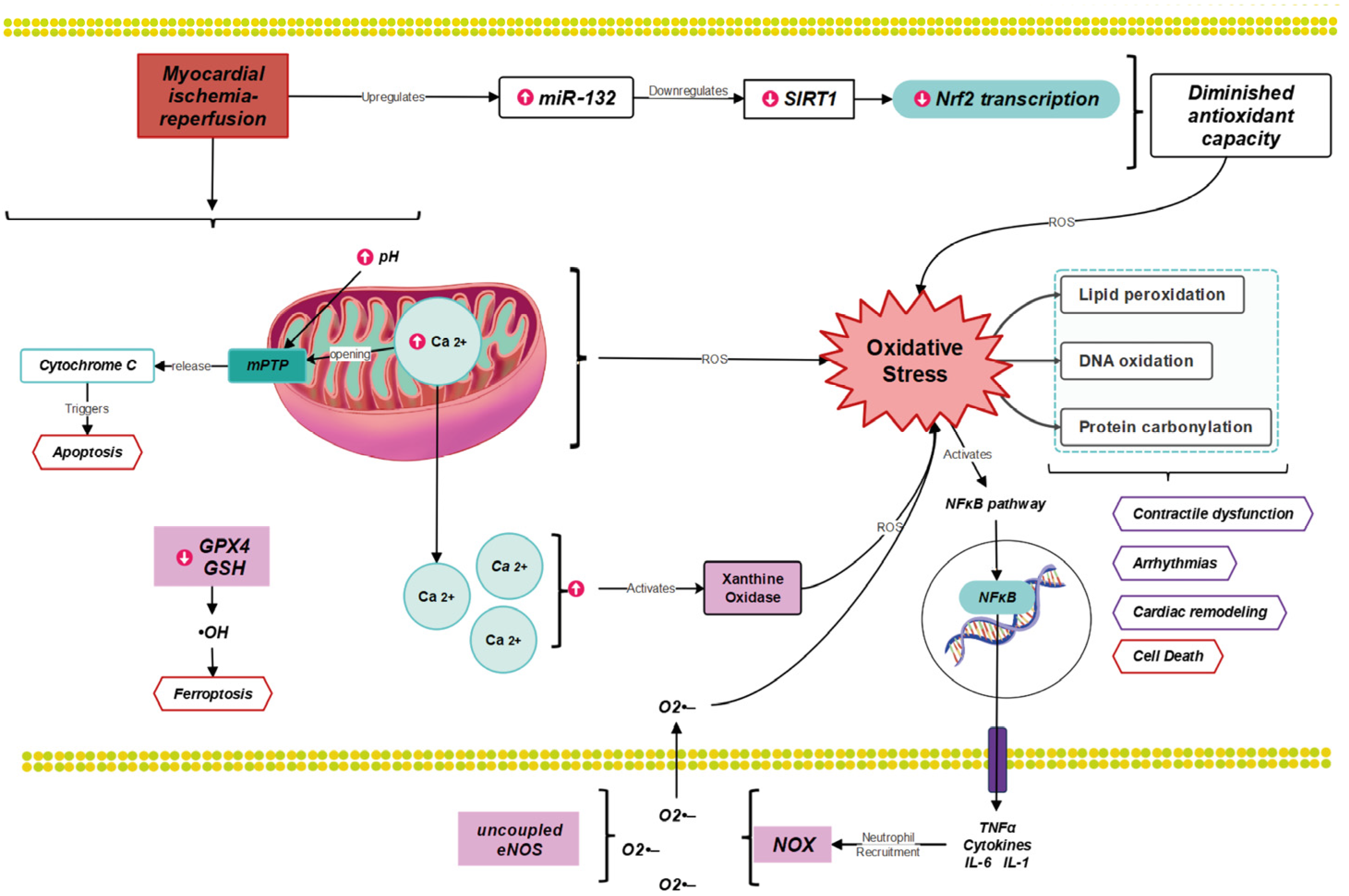
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
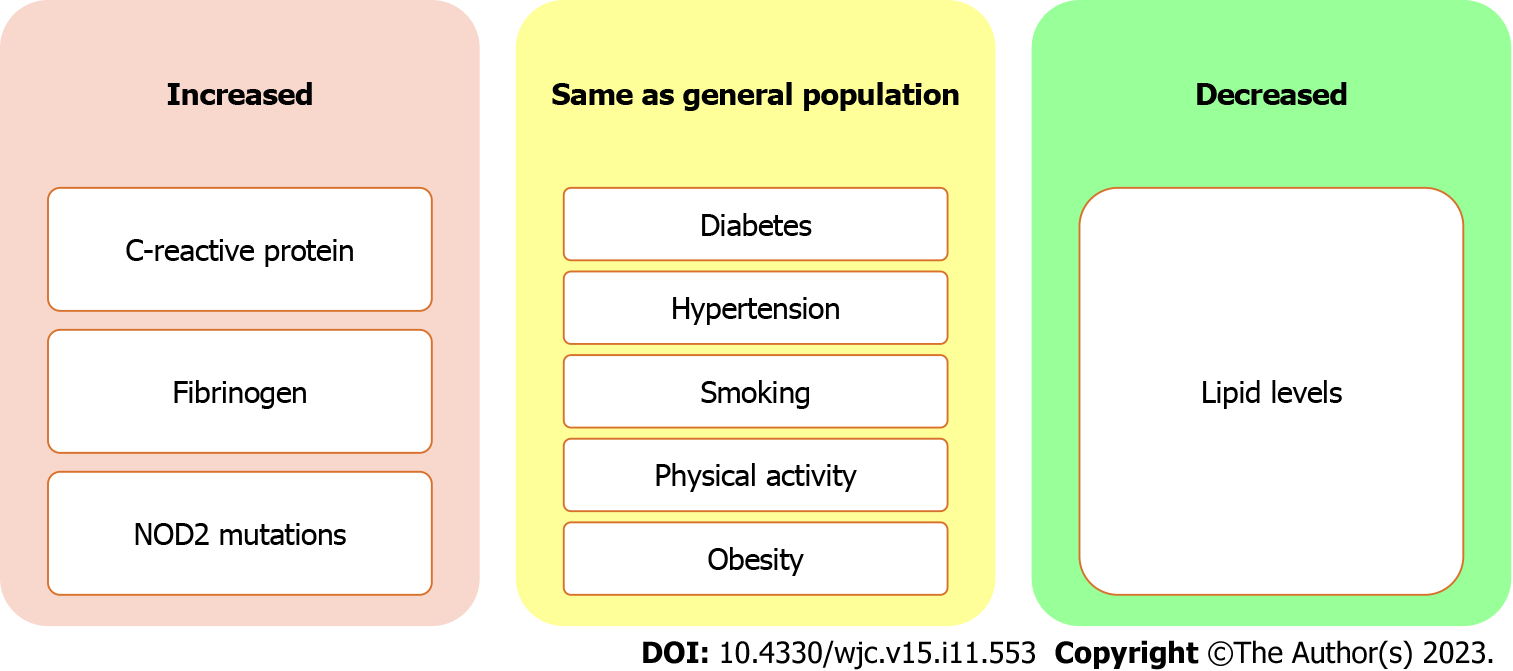
Cardiovascular implications of inflammatory bowel disease: An updated review
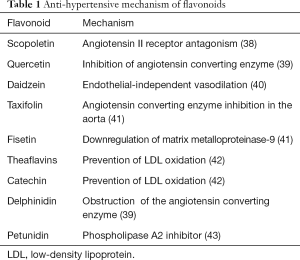
The role of flavonoids in the prevention and management of cardiovascular complications: a narrative review - Chen - Annals of Palliative Medicine