Nitric oxide (NO) cycle. NO2⁻: nitrite anion; NO3⁻: nitrate anion; NO
4.9 (484) · € 20.99 · Auf Lager

Release of Nitrous Acid and Nitrogen Dioxide from Nitrate Photolysis in Acidic Aqueous Solutions

Decrease of nitrogen cycle gene abundance and promotion of soil microbial-N saturation restrain increases in N2O emissions in a temperate forest with long-term nitrogen addition - ScienceDirect

SOLVED: The nitrite ion (NO2^-) in soil is oxidized to nitrate ion (NO3^-) by the bacteria Nitrobacter agilis in the presence of oxygen. The half-reduction reactions are NO3^-+2 H^++2 e^-⟶NO2^-+H2O E^∘=0.42 V

Nitrogen Cycle - Wastewater Treatment - Climate Policy Watcher

The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics
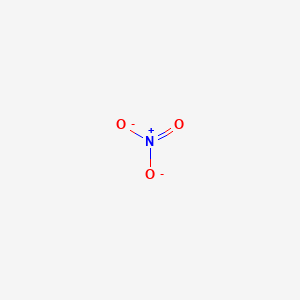
Nitrate, NO3

Nitric oxide (NO) cycle. NO2⁻: nitrite anion; NO3⁻: nitrate anion; NO

Nitric oxide (NO) cycle. NO2⁻: nitrite anion; NO3⁻: nitrate anion; NO

Solved Nitric oxide reacts rapidly with unstable nitrogen
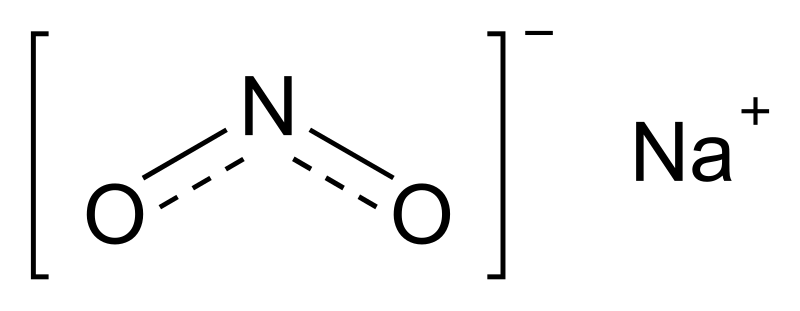
Sodium nitrite - Wikipedia

Recent Advances in Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation Reactions on Copper‐Based Catalysts - Zheng - Advanced Materials - Wiley Online Library

Solved 18.129 The nitrite ion NO2 in soil is oxidized to the











